
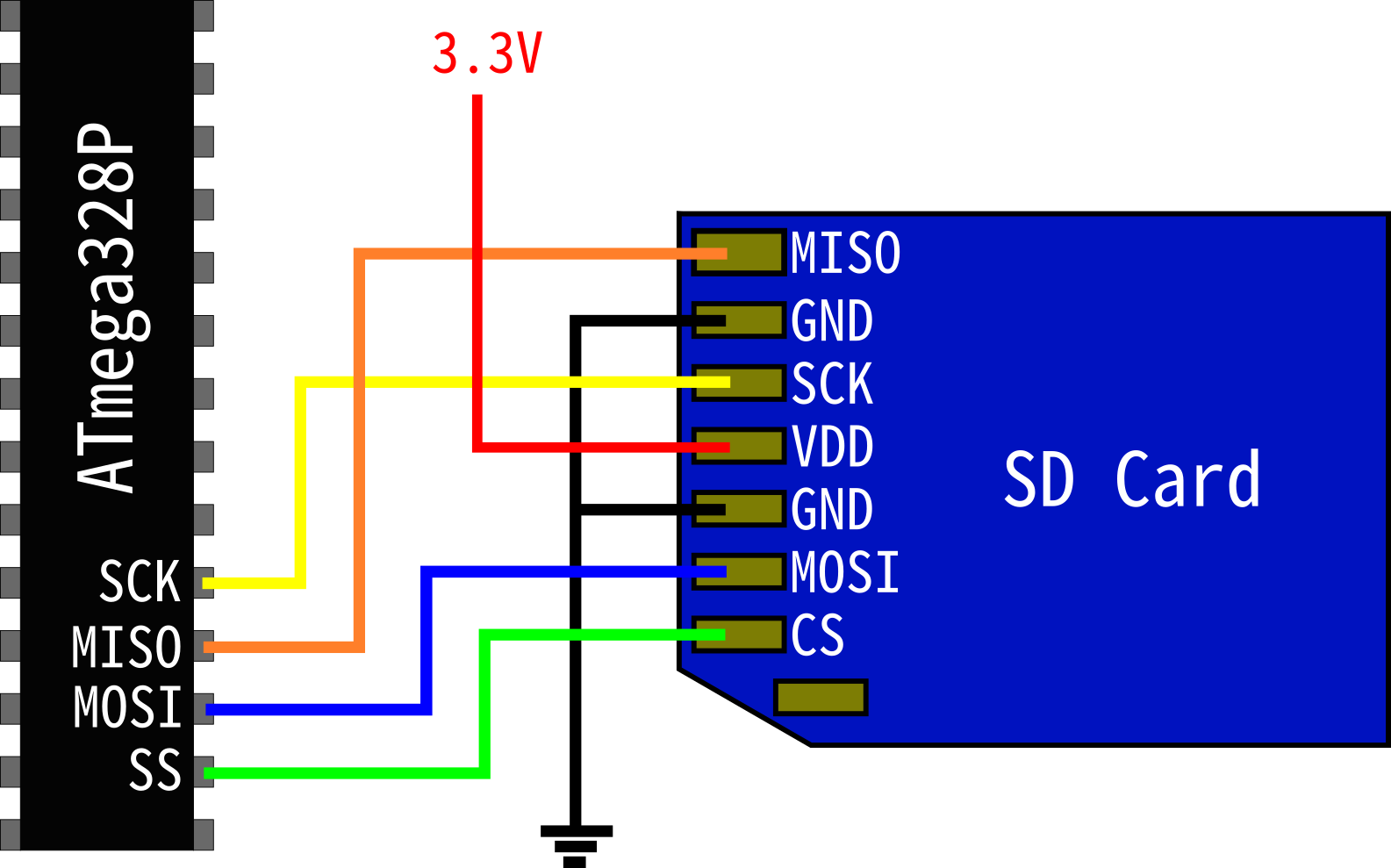
The designs of these step-down and step-up circuits were taken from the final project by Peter D'Antonio and Daniel Riiff. Likewise, the output from the card was fed through a step-up circuit before going to B.6. The three inputs to the card were each fed through separate step-down circuits to decrease the voltage from the power supply's 5V to the 3.3V required by the card. We wired the SD card connector's clock, DataIn, and ChipSelect pins to PORTB's pins 7, 5, and 0, respectively, and the DataOut to PORTB pin 6. We connected it to the STK500 with a 10-pin jumper cable to PORTB, which contains the Mega32's SPI interface. In addition, we built a circuit to connect to the SD/MMC card. We ran kaOS on an Atmel Mega32 on an STK500 development board, which are available in the lab. These features, although useful bells and whistles, were cut from the design because they were extraneous to our core vision of creating a dynamically-loading OS, added unnecessary complexity, and consumed extra flash and RAM, which might be needed for some user programs. In designing the operating system, we considered various library functions that we could add to increase functionality, such as LCD and keypad drivers, events, and support for multiple programs on a single card with a menu system to choose between them. Additional information about SD card communication and the SPI protocol were obtained from SanDisk's SD card manual.
CODEVISION SDCARD PROJECTS CODE
Also, portions of our code used to read from SD/MMC cards were adapted from code written by Radig Ulrich. In particular, we used his context-switching code to swap processor states when changing threads.

While the idea for this project was born out of the lack of a true OS for the Mega32 that dynamically loads programs, we must give some credit to aOS, created by Anssi Ylätalo. kaOS also supports messaging between threads as a means of inter-thread communication. Threads with the same priority are alternately preempted to give both equal processing time. It supports creation of up to 8 threads, which can be prioritized. The operating system is real-time, multithreaded, and preemptive. Once kaOS loads a program, it creates a thread for it and jumps to its main() method. This gives it write access to other portions of flash memory so that it can write executables to program space. The program loader resides in the Mega32's bootloader section of flash. These programs can be written similar to a standard Atmel Mega32 program, except that it must include the kaos.h header file, which provides an interface to the threading and messaging calls to the OS. The card reader is accessed via the Atmel's SPI interface by the program loader, which places the program into flash memory.

The design of kaOS was broken up into two major components: the operating system itself and the card reader and program loader.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
